Connected mode
Connecting SonarQube for IDE to SonarQube Server, SonarQube Cloud, or SonarQube Community Build is the first step in setting up the Sonar Solution, to take advantage of having consistent issues reported on both sides. Setting up connected mode will permit the transmission of information SonarQube for IDE needs, such as URLs and user credentials or file exclusions and marked issues, to communicate with SonarQube (Server, Cloud) or SonarQube Community Build. When binding your local workspace folder to your SonarQube (Server, Cloud) or SonarQube Community Build project(s), SonarQube for IDE will try to match, as much as possible, the same rules and settings as found on the server.
While in connected mode, SonarQube for IDE receives notifications from SonarQube (Server, Cloud) or SonarQube Community Build about your quality gate changes and new issues. Smart notifications can be enabled or disabled from the UI while creating or editing the connection settings.
Setting up connected mode is easy and you can easily share your connection setup with your team.
Benefits
- Analyze more languages and detect more issues by combining SonarQube for Visual Studio’s supported rules with those supported by SonarQube Server, SonarQube Cloud, and SonarQube Community Build.
- Highlight advanced issues (in the IDE) like injection vulnerabilities, detected by SonarQube Server and SonarQube Cloud.
- An issue discovered in SonarQube (Server, Cloud) or SonarQube Community Build can be quickly opened in the IDE via a dedicated button.
- Use the same quality profile locally as is defined on the SonarQube Server, SonarQube Cloud or SonarQube Community Build server. You'll also see rules in the same rule mode as defined in SonarQube Server or SonarQube Community Build.
- Apply settings, such as rule selection and file exclusions defined on the SonarQube Server, SonarQube Cloud, or SonarQube Community Build server to your local analysis.
- Define specific analyzer parameters in SonarQube Server, SonarQube Cloud, or SonarQube Community Build and have those parameters applied locally.
- Changes in your SonarQube Server, SonarQube Cloud, or SonarQube Community Build quality gate will arrive in your IDE when you accept Smart notifications.
- Automatically suppress issues that are marked as Accepted or False Positive in SonarQube Server, on SonarQube Cloud, or in SonarQube Community Build so that locally reported issues match those found on the server.
When running in connected mode with SonarQube Server 10.4 or newer, Won’t Fix becomes Accept.
Connected mode does not push issues to the server. Rather, its purpose is to configure the IDE so that it uses the same settings, as much as possible, as it is defined on the server.
Free and open-source versions of SonarQube Server and SonarQube Cloud are available to work in connected mode. In SonarQube Cloud, it’s always free to analyze your publicly accessible projects; subscription plans are required only if linking to a private repository.
Prerequisites and supported languages
Having a SonarQube Server project (in an Active version), a SonarQube Cloud project, or a SonarQube Community Build project is required to run SonarQube for Visual Studio in connected mode. The following languages and Visual Studio project types are supported:
- C# rules (.csproj)
- VB.NET rules (.vbproj)
- C++ rules (*.vxcproj and CMake)
- CSS rules (from SonarLint for Visual Studio v6.16)
- JavaScript rules and TypeScript rules in MSBuild projects or folder workspaces (from SonarLint for Visual Studio v6.7)
- Secrets rules
When running SonarQube for Visual Studio in connected mode with SonarQube Server or SonarQube Community Build, security hotspots found in JS and CFamily files will be reported. See the Security hotspot page for more details.
Branch awareness
Branch awareness allows SonarQube for IDE to consider the branch currently checked out in the IDE and synchronize it with the most appropriate branch from the SonarQube (Server, Cloud) or SonarQube Community Build; we call this branch matching.
In Connected Mode, SonarQube for IDE synchronizes some data from the issues found on the server, such as the issue's status and resolution. It is important that SonarQube for IDE knows which branch the user is on at that moment to sync the local analysis with the correct branch analyzed by SonarQube (Server, Cloud) or SonarQube Community Build.
SonarQube for Visual Studio only supports git and the git branch name with regard to branch matching. If the SonarQube for Visual Studio’s branch awareness algorithm fails to detect a best match, injection vulnerabilities, and issue suppressions will be pulled from the SonarQube (Server, Cloud) main branch by default.
Checking which branches are analyzed on the server
In SonarQube Server, open the highlighted drop-down list shown below (as it looks in SonarQube Server) for a list of analyzed branches and pull requests.
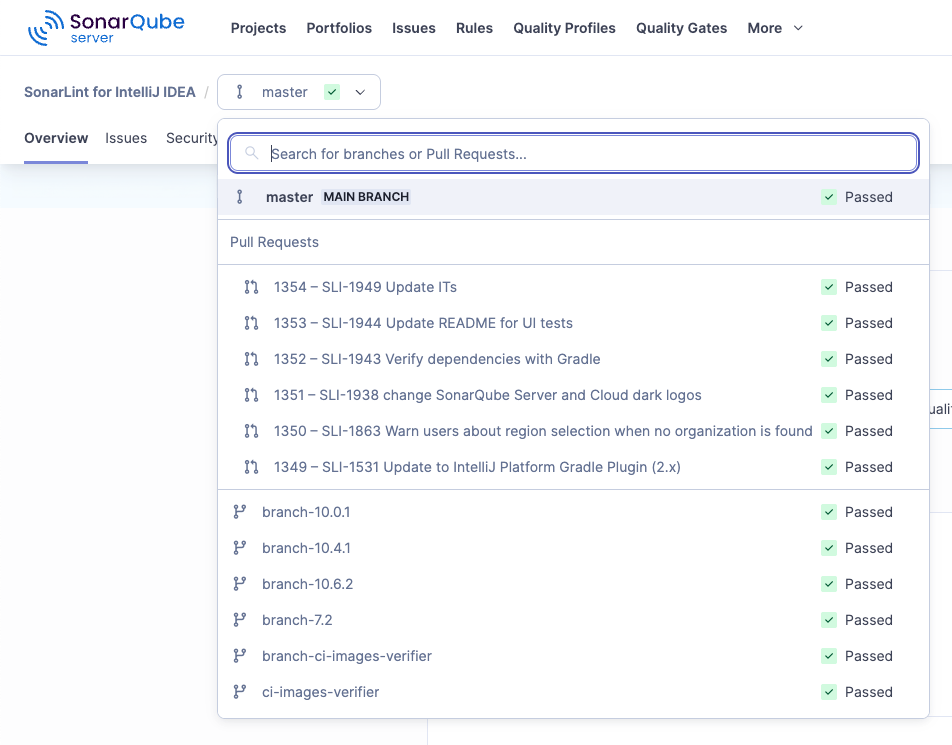
To analyze branches other than master|main , please check the SonarQube Server or SonarQube Cloud documentation about branch analysis.
How SonarQube for IDE selects which branch to sync
SonarQube for IDE deploys these three methods to choose which branch (in SonarQube (Server, Cloud)) to sync with the local analysis.
Exact match
Branches with the same name are considered the same branch. If the branch that is currently checked out locally is analyzed on the server, SonarQube for IDE will pick this branch for synchronization.
Closest branch
SonarQube for IDE will consider all local branches that also exist on the server. For each branch, SonarQube for IDE will compute the distance between the current HEAD and the branch by the count of commits. The closest branch will be kept. In case the number of commits is the same for two or more branches and the main branch is among them, it will be preferred; otherwise, the tie will be broken with a random choice (from the list of equidistance branches).
Default to main branch
All other cases will default to the branch marked as "main" on the server. For example, if there is an error in reading the branch, or if there is no Git repo, SonarQube for IDE will default to the main branch.
Long and short-lived branches
When using Connected Mode with SonarQube Cloud, issues on short-lived branches are not synchronized. When an issue is marked in SonarQube Cloud accepted or false positive on a short-lived branch, SonarQube for IDE will still show that issue in the IDE.
SonarQube Server does not distinguish between long- and short-lived branches therefore, all issue resolutions are recognized.
Connection setup
SonarQube for Visual Studio provides a connection wizard to help you set up connected mode with SonarQube (Server, Cloud) or SonarQube Community Build. Please see the Connected mode setup page for detailed instructions to set up connected mode and bind your project.
Sharing your setup
From version 7.4, it is possible to share a setup configuration file with your team, simplifying the process.
One team member must step through the first-time setup process, then export and commit the binding configuration to the repository. Any team member running SonarQube for Visual Studio will find the binding details inside of the project’s source folder and automatically receive a notification to bind the project.
Please see the Connected mode setup page for detailed instructions.
Project binding
When you bind a project, SonarQube for Visual Studio uses the Quality Profile defined on the server to decide which rules to run locally, and which rule parameters to use. When you mark a particular issue as “safe” or “won’t fix” on the server, the corresponding issue will be ignored in the IDE. Check the SonarQube Server, SonarQube Cloud, or SonarQube Community Build documentation for details about managing your quality profile.
When running in connected mode with SonarQube Server 10.4 or newer, Won’t Fix becomes Accept.
Local settings
If you are running SonarLint for Visual Studio v6.16 or earlier, please see the Previous versions page for information about how server synchronization is managed. Before v7.0 (released in June 2023), connected mode behaved a bit differently; check the Migrate connected mode to v7 page for more details.
Types of updates
Quality Profiles
Quality profiles are a key part of using SonarQube for Visual Studio in connected mode with SonarQube Server, SonarQube Cloud, or SonarQube Community Build. SonarQube for Visual Studio periodically syncs the project’s quality profile from the server and applies its set of rules during code analysis.
Other types of updates
Suppressed issues
As mentioned above, it is rare that you will need to manually retrieve suppressed issues from the server because SonarQube for Visual Studio automatically fetches them when the bound solution is opened. From v6.14, SonarQube for Visual Studio supports near-real-time sync of suppressed issues; note that previous releases periodically check for updates every 10 minutes, when a bound solution is opened, or the git branch changes in the IDE.
Issue suppressions are reapplied automatically.
If the code is different from when it was analyzed by SonarQube (Server, Cloud) or SonarQube Community Build, a suppressed issue might still appear in Visual Studio.
File exclusions
When running in connected mode, SonarQube for Visual Studio will fetch file exclusions from SonarQube Server or SonarQube Cloud when you bind a project. These settings are saved to a file named sonar.settings.json.
Note that in SonarLint for Visual Studio 7.0, the settings file was moved outside of the solution directory; please check the Legacy Connected Mode article on the Previous versions page for information about the settings file in versions 6.16 and older.
For more information about how SonarQube for Visual Studio settings are handled by the server, see the SonarQube Server, SonarQube Cloud, or SonarQube Community Build documentation on setting your analysis scope.
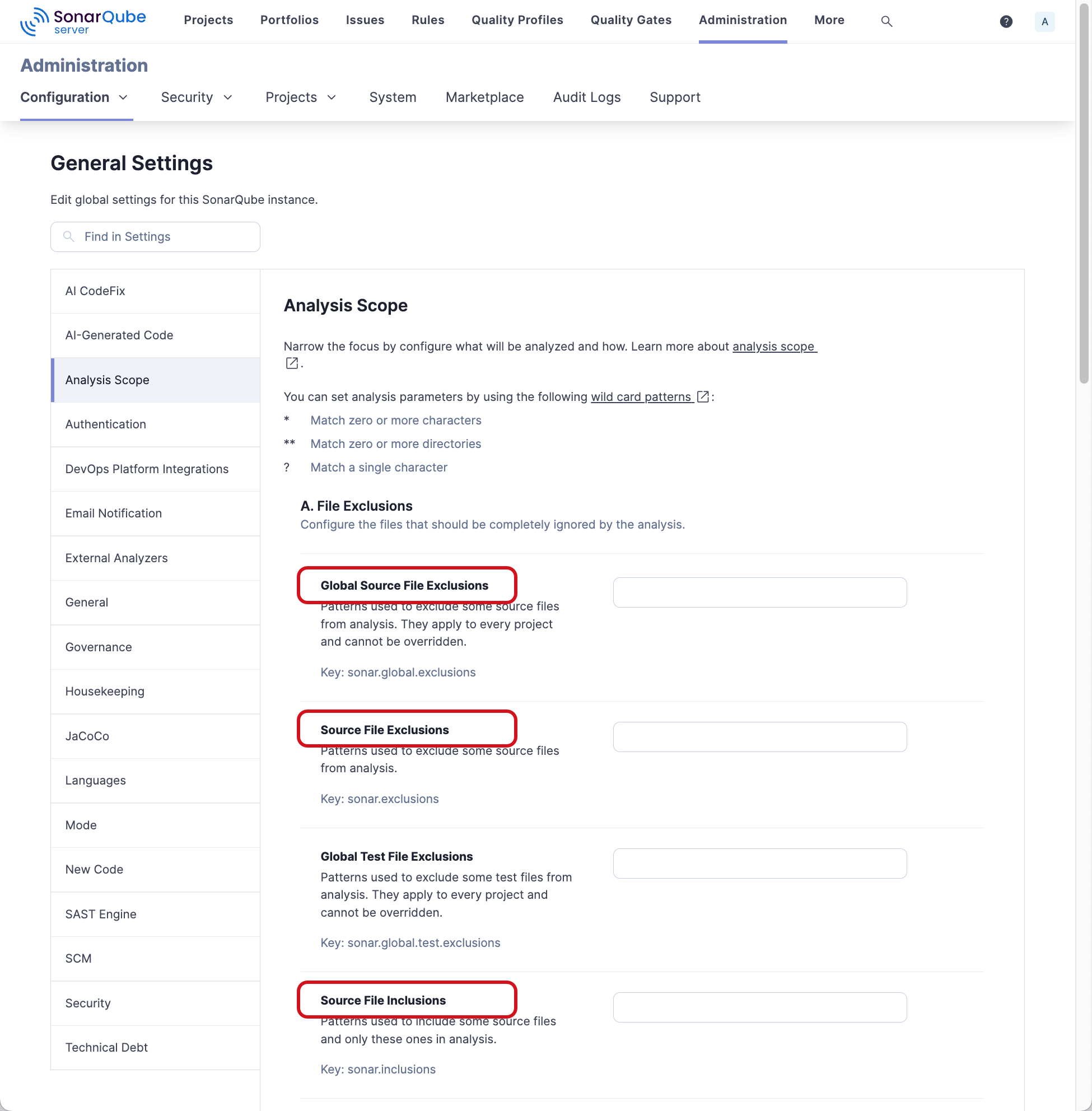
Known limitations for file exclusions:
- Supported Languages: C# & VB (.NET support in SonarLint v6.15+), C, C++, CSS, JavaScript, TypeScript, and Secrets.
- Patterns should start with
**/ - Multicriteria and Test exclusions are not supported. SonarQube for Visual Studio only supports Global Source File Exclusions, Source File Exclusions, and Source File Inclusions when setting the analysis scope. For more information about file inclusion and exclusion, see the pages about file inclusion and exclusion in the SonarQube Server, SonarQube Cloud, or SonarQube Community Build documentation.
Known issues
The goal is to have the same issues reported in the IDE as are reported on the server. However, there are a number of reasons why a set of issues can be different: some technical, some bugs, or some work that just hasn't been done yet.
See ticket #1336 for a summary of the known issues and their current status.
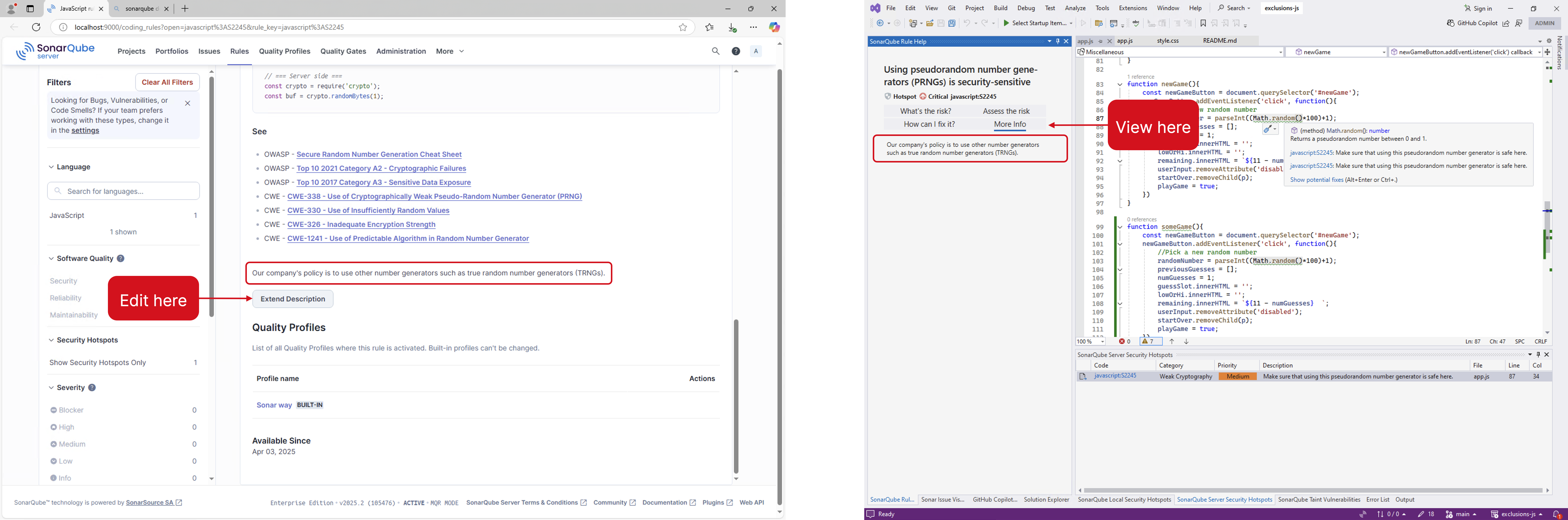
Extended Rule descriptions
From v6.14 and newer, Extended rule descriptions written in SonarQube (Server, Cloud) or SonarQube Community Build are available in the Sonar Rule Help view container. Because they are written in SonarQube (Server, Cloud) or SonarQube Community Build, you must be viewing your project while in connected mode.
- You can extend rule descriptions in SonarQube Server, SonarQube Cloud, or SonarQube Community Build to let users know how your organization uses a particular rule or to give more insight into a rule.
- Note that the extension will be available to non-admin users as a normal part of the rule details.
In your SonarQube (Server, Cloud) or SonarQube Community Build instance, go to the Rule you want to edit in the Rules tab, then click the Extend Description button to open a field box that will accept your Markdown-formatted text. What you add to the rule from your SonarQube (Server, Cloud) or SonarQube Community Build server will be seen in your instance of SonarQube for Visual Studio.
Legacy Connected Mode
Before SonarLint for Visual Studio version 7.0 (released in June 2023), connected mode behaved a bit differently:
- In versions 6.16 and earlier, SonarLint saved all of its configuration files inside the solution project folder, and it was up to the user to commit or exclude the Sonar settings. This caused some version control management problems, especially when syncing with the server in connected mode. Please check the Previous versions page for important details when running in connected mode.
- From version 7.0 and newer, the settings folder was moved outside of the solution directory to the
%AppData%\Roaming\SonarLint for Visual Studio\Bindingsfolder.
Before SonarLint for Visual Studio version 4.0 (released in May 2018), connected mode behaved a bit differently:
- The appropriate NuGet package for the
SonarAnalyzer.CSharp/SonarAnalyzer.VisualBasicanalyzers were added to each project. - The connected mode settings were saved in a solution-level folder called SonarQube in a file called
SolutionBinding.sqconfig. - If you are upgrading to version 7.0 from Sonarlint version 3.10 or earlier, please check the Migrating from a legacy version paragraph for instructions.
In SonarLint for Visual Studio version 4.0 and later:
- The analyzer NuGet packages are no longer installed in any project
- The settings are saved in a solution-level folder called
.sonarlintin a file called[solution name].slconfig.
SonarQube for IDE-SonarQube Server version support policy
SonarQube for IDE enables users to establish a connection to the latest SonarQube Server version and to the latest LTA (Long-Term Active) version. When a new LTA version is released, we still enable connecting SonarQube for IDE to the previous LTA version for a certain period of time (currently 9 months after the latest LTA release) to allow enough time for organizations to update their SonarQube Server version.
For more information about long-term support of SonarQube Server, check out our page describing the SonarQube Server release model. Review your SonarQube for IDE-specific requirements for version-to-version differences.
⚠️ The 8.9LTA reached its support expiration date (in November ’23).
Notifications
Connected mode allows SonarQube (Server, Cloud) and SonarQube Community Build to send smart alerts to individuals or teams as soon as something appears on the server that something failed, when new issues are discovered or when the Sonar Quality Profile is updated, for example. With everyone in the loop, issues can be addressed promptly, improving the overall software quality and delivery. The notification will include a link to call back to SonarQube (Server, Cloud) and SonarQube Community Build where you can learn more about the issues that were introduced.
You'll receive smart notifications in your IDE when:
- the quality gate status of a project open in your IDE changes (see the SonarQube Server, SonarQube Cloud, or SonarQube Community Build documentation for details about using quality gates in your project)
- a SonarQube (Server, Cloud) and SonarQube Community Build analysis raises new issues that you've introduced in a project open in your IDE
You can activate or deactivate smart notifications in SonarQube for IDE on the IDE side for a server-by-server basis.
Sonar Smart Notifications are available in all editions of SonarQube (Server, Cloud) and SonarQube Community Build.
Was this page helpful?