TLS certificates on client side
If your SonarQube Server instance is secured, add the self-signed certificate to the CI/CD host. If mutual TLS is used, an additional setup is required.
If your SonarQube Server instance is secured behind a proxy and a self-signed certificate, then you must add the self-signed certificate to the trusted CA certificates of the SonarScanner.
In addition, if mutual TLS is used then you must define the access to the client certificate at the SonarScanner level.
Managing the self-signed server certificate
Introduction to server authentication
During the TLS authentication of the server, the client requests the server certificate from the server and verifies that this certificate is signed by a CA it trusts by checking its TrustStore. In case a self-signed server certificate is used, it must be added to the TrustStore of the client. The figure below shows the certificates involved in the authentication of SonarQube Server by the SonarScanner.
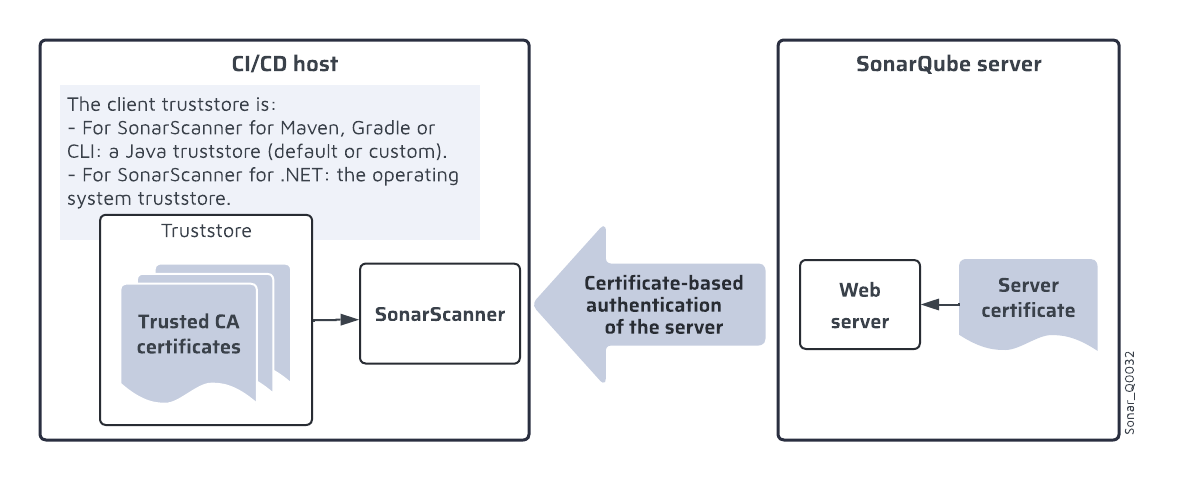
Adding the self-signed server certificate to the trusted CA certificates
Step 1: Add the certificate for your scanner
The way you add your self-signed certificate depends on your scanner.
You can either:
Insert your certificate in the default JVM TrustStore (something like
\jre\lib\security\cacerts). To add the self-signed server certificate to the default TrustStore, use the JVM tool keytool. The instructions depend on your operating system and you will find many resources online, such as this one for Linux.
or:
Provide a custom Java TrustStore. This operation depends on your scanner version:
Version >= 5.0: We recommend using the properties
sonar.scanner.truststorePathandsonar.scanner.truststorePassword. If this does not work, please retry after upgrading to the next scanner minor version. You can also use the properties described below for version <= 4.0.Version <= 4.0: Use the following properties:
javax.net.ssl.trustStore: path to the TrustStore file (pkcs12 format is recommended).javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword: password of the TrustStore.
The javax.net property is a JVM property, not a scanner property. It should be passed using the SONAR_SCANNER_OPTS environment variable. For example: SONAR_SCANNER_OPTS="-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=C:/ssl/truststore.p12 -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=changeit" (on Windows, use forward slashes as path separators).
This scanner is still relying on the Java VM for the SSL configuration.
You can either:
Insert your certificate in the default JVM TrustStore (something like
\jre\lib\security\cacerts). To add the self-signed server certificate to the default TrustStore, use the JVM tool keytool. The instructions depend on your operating system and you will find many resources online, such as this one for Linux.
or:
Provide a custom Java TrustStore by using the following properties:
javax.net.ssl.trustStore: path to the TrustStore file (pkcs12 format is recommended).javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword: password of the TrustStore.
The javax.net property is a JVM property, not a scanner property. It should be passed using the SONAR_SCANNER_OPTS environment variable. For example: SONAR_SCANNER_OPTS="-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=C:/ssl/truststore.p12 -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=changeit" (on Windows, use forward slashes as path separators).
The operation depends on the version of your SonarScanner for .NET.
Scanner version > = 10.0
You can use a PKCS#12 keystore as explained below.
The SonarScanner for .NET 10.0+ does not support a certificate revocation list (CRL) when the issuing certificate authority is given via the TrustStore file. This means that revoked certificates will still be trusted when the issuing certificate is given via the TrustStore file. To benefit from CRL, you can still use the method described for Scanner version <= 9.1 below.
Consider the following when generating the PKCS#12 keystore:
The default location for the TrustStore is
$SONAR_USER_HOME/ssl/truststore.p12(default value for SONAR_USER_HOME is ~/.sonar). This location can be overridden using the propertysonar.scanner.truststorePath.The default password for the TrustStore is
changeit. This password can be overridden using the propertysonar.scanner.truststorePassword.
To override the default parameters, set the sonar properties in the begin step, and, for the password, also in the end step.
Generating the PKCS#12 keystore
If you have a PEM or DER certificate, you can use OpenSSL or Keytool to generate the PKCS #12 keystore:
With OpenSSL:
With Keytool
Scanner version < = 9.1
You must use the operating system TrustStore. Proceed as follows:
From scanner version 7.0, disable JRE auto-provisioning (JRE auto-provisioning is not compatible with the system TrustStore if you use SonarScanner for .NET). To do so, see Disabling JRE auto-provisioning.
Add the self-signed server certificate to the operating system TrustStore:
On Linux:
Copy the self-signed server certificate to
/usr/local/share/ca-certificates.Run
sudo update-ca-certificates.
On macOS: use Keychain Access or use the following command:
On Windows: use certutil. Here is an example:
Add the self-signed certificate to the Java TrustStore for SonarScanner CLI (which is used by SonarScanner for .NET) as explained in the SonarScanner for NPM or CLI tab, for SonarScanner CLI < 6.0.
The operation depends on the version of your SonarScanner for NPM or SonarScanner CLI.
SonarScanner for NPM >= 4.0 and SonarScanner CLI >= 6.0
You must provide a PKCS#12 keystore.
Consider the following when generating the PKCS#12 keystore:
The default location for the TrustStore is
$SONAR_USER_HOME/ssl/truststore.p12(default value for SONAR_USER_HOME is ~/.sonar). This location can be overridden using the propertysonar.scanner.truststorePath.The default password for the TrustStore is
changeit. This password can be overridden using the propertysonar.scanner.truststorePassword.
Generating the PKCS#12 keystore
If you have a PEM or DER certificate, you can use OpenSSL or Keytool to generate the PKCS #12 keystore:
With OpenSSL:
With Keytool
If running the scanner in Docker: use a mounted volume
The preferred way is to mount a folder containing the PKCS #12 file under /opt/sonar-scanner/.sonar/ssl.
SonarScanner for NPM < 4.0 and SonarScanner CLI < 6.0
This scanner is still relying on the Java VM for the SSL configuration.
You can either:
Insert your certificate in the default JVM TrustStore (something like
\jre\lib\security\cacerts). To add the self-signed server certificate to the default TrustStore, use the JVM tool keytool. The instructions depend on your operating system and you will find many resources online, such as this one for Linux.
or:
Provide a custom Java TrustStore by using the following properties:
javax.net.ssl.trustStore: path to the TrustStore file (pkcs12 format is recommended).javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword: password of the TrustStore.
The javax.net property is a JVM property, not a scanner property. It should be passed using the SONAR_SCANNER_OPTS environment variable. For example: SONAR_SCANNER_OPTS="-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=C:/ssl/truststore.p12 -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=changeit" (on Windows, use forward slashes as path separators).
For information about setting the mentioned sonar properties, see Using the scanner for .NET, Configuring the scanner for NPM, or the SonarScanner CLI pages.
Step 2: Additional step depending on your CI tool
If you use GitHub Action or Azure Pipelines, an additional step is necessary as described below.
If you use the sonarqube-scan-action for your GitHub Action and your SonarQube Server instance has certificates that need to be recognized by the GitHub runner, you’ll need to set the SONAR_ROOT_CERT environment variable in GitHub.
To do this, go to your GitHub repository > Settings > Secrets and Variables and add the SONAR_ROOT_CERT environment variable in PEM format. You can also add it at the level of your GitHub organization (recommended).
Due to a known GitHub issue, if your GitHub Action v4 and above
uses
SONAR_ROOT_CERTand is executed in a containerized environment, for example when the job running the action declares
container: <docker-image-name>
you need to explicitly set the SONAR_USER_HOME environment variable to be the "$HOME/.sonar".
You can do that by adding the following step before executing the action:
If you want to add the SonarQube analysis to your Azure build pipeline and your SonarQube Server instance uses a self-signed certificate, you must provide the server certificate so that the AzureDevOps Extension for SonarQube can connect to SonarQube Server during the Prepare Analyze Configuration and Run Code Analysis tasks.
Proceed as follows:
Define the following environment variable (this setup is required for the Prepare Analyze Configuration task):
Key:
NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTSValue: path to the certificate
Make sure you have added the certificate for the SonarScanner used with your Azure DevOps extension (SonarScanner for Maven, Gradle, .NET, or CLI) as described above in Step 1.
Managing the client certificates
Introduction to client authentication
If mutual TLS is used then both the client and the server authenticate the other party. During the TLS authentication of the client, the client must provide its certificate with the corresponding CA certificate chain (intermediate and root CA certificates) to the server. The client manages its certificates in its own keystore. The figure below shows the certificates involved in SonarQube Server’s TLS authentication of the SonarScanner.
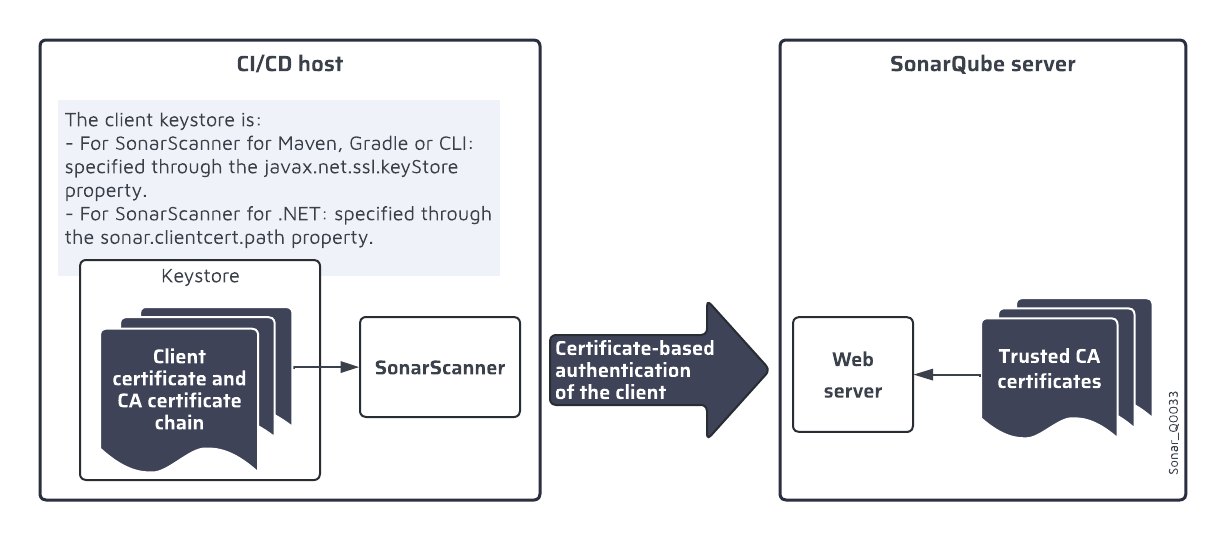
Defining the access to the client certificates
For SonarScanner for Maven, Gradle, CLI, or NPM
Store the client certificate and CA certificate chain in a keystore file and define the access to this file through the following properties:
javax.net.ssl.keyStoreor (for SonarScanner CLI from version 6.0 and SonarScanner for NPM from version 4.0)sonar.scanner.keystorePath: path to the keystore file.javax.net.ssl.keyStorePasswordor (for SonarScanner CLI from version 6.0 and SonarScanner for NPM from version 4.0)sonar.scanner.keystorePassword: password of the keystore file.
For SonarScanner for .NET
Store the client certificate and CA certificate chain in a keystore file and define the access to this file through the following properties:
sonar.clientcert.path: path to the keystore file, must be set in the begin step.sonar.clientcert.password:password of the keystore file, must be set in both the begin and end steps.
In addition, set the following options before the end step (for the SonarScanner CLI invocation):
javax.net.ssl.keyStore: same value assonar.clientcert.pathjavax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword: same value assonar.clientcert.password
Related pages
Was this helpful?

