Webhooks
This feature is available starting in Team plan.
Introduction to webhooks
Webhooks notify external services when:
- A project analysis is complete.
This is done regardless of the status of the background task or of the quality gate. - An issue type, severity, or status is updated, and this update changes the quality gate status.
For example:- A user marks an issue as False Positive and the quality gate status turns green.
- The severity of an issue is increased and the quality gate status turns red.
An HTTP(S) call including a JSON payload is sent to each configured URL. URLs may be specified at both the project and global levels. The project-level specification does not replace global-level webhooks. All hooks at both levels are called.
HTTP(S) call
The HTTP(S) call:
- Has an HTTP header
X-SonarQube-Projectwith the project key to allow quick identification of the project involved. - Includes a JSON document as payload, using the POST method. See below.
- Has a content type of
application/json, with UTF-8 encoding.
Payload
The payload is a JSON document that includes:
analysedAt: when the analysis was performed.project: the identification of the project analyzed.qualityGate: each quality gate criterion checked and its status.qualityGate.status: the quality gate status of the analysis.statusandtaskID: the status and the identifier of the background task.properties: user-specified properties.
You can define project parameters to be added to the payload.
Payload example
{
"serverUrl": "<mySonarqubeURL>",
"taskId": "AVh21JS2JepAEhwQ-b3u",
"status": "SUCCESS",
"analysedAt": "2016-11-18T10:46:28+0100",
"revision": "c739069ec7105e01303e8b3065a81141aad9f129",
"project": {
"key": "myProject",
"name": "My Project",
"url": "https://mycompany.com/sonarqube/project/overview?id=myproject"
},
"properties": {
},
"qualityGate": {
"conditions": [
{
"errorThreshold": "1",
"metric": "new_security_rating",
"onLeakPeriod": true,
"operator": "GREATER_THAN",
"status": "OK",
"value": "1"
},
{
"errorThreshold": "1",
"metric": "new_reliability_rating",
"onLeakPeriod": true,
"operator": "GREATER_THAN",
"status": "OK",
"value": "1"
},
{
"errorThreshold": "1",
"metric": "new_maintainability_rating",
"onLeakPeriod": true,
"operator": "GREATER_THAN",
"status": "OK",
"value": "1"
},
{
"errorThreshold": "80",
"metric": "new_coverage",
"onLeakPeriod": true,
"operator": "LESS_THAN",
"status": "NO_VALUE"
}
],
"name": "SonarQube way",
"status": "OK"
}
}Webhook protection with HMAC
SonarQube can generate an HMAC to allow the third party service to verify the integrity and authenticity of the webhook they receive. To do so, it uses the HMAC-SHA256 algorithm and the secret stored in the webhook configuration.
Configuring webhooks
This paragraph explains how to configure webhooks in the UI. You can also use the Web API.
You can configure up to 10 webhooks at the project level and at the organization level. If configured, all 20 webhooks will be executed.
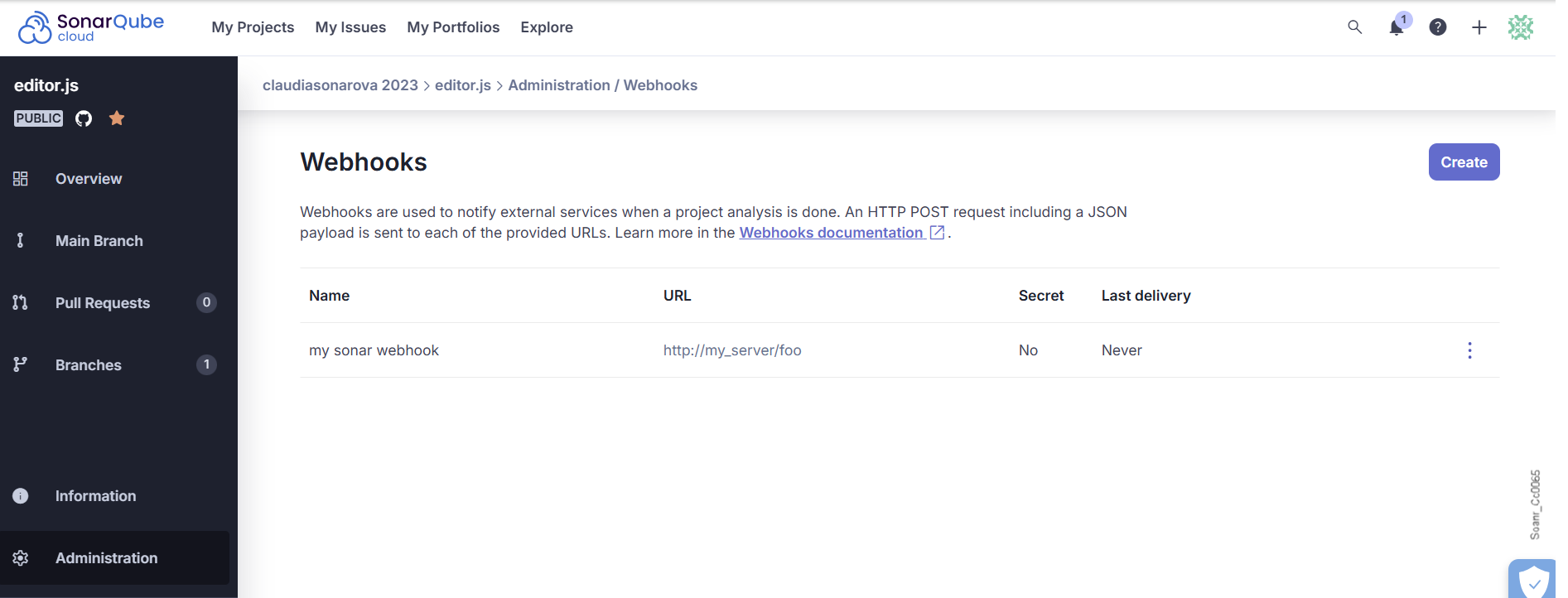
Configuring webhooks for your project
You must be a project admin.
Proceed as follows:
- Retrieve your project.
- Go to Administration > Webhooks.
- Select Create. The Create Webhook dialog is displayed.
- Enter the webhook name.
- Enter the URL to which the webhook is to be delivered.
- Enter a secret if you want to protect the webhook with HMAC. See Securing your webhooks below.
- To update or delete a webhook, select the corresponding command in the three-dot menu at the far right of the webhook row.
Configuring webhooks for your organization
You must be an organization admin.
Proceed as follows:
- Retrieve your organization.
- Go to Administration > Configuration > Webhooks.
- Select Create. The Create Webhook dialog is displayed.
- Enter the webhook name.
- Enter the URL to which the webhook is to be delivered. You can provide user/password in the URL as described in Securing your webhooks below.
- Enter a secret if you want to protect the webhook with HMAC. See Securing your webhooks below.
- To update or delete a webhook, select the corresponding command in the three-dot menu at the far right of the webhook row.
Testing the webhooks
It's important that you test your configured webhooks. To do so, you can use various webhook testing/debugging tools.
Monitoring the webhook delivery
You can monitor the delivery of your webhooks configured at the project or organization level in the SonarQube UI. You can also use the Web API to retrieve the webhook deliveries.
Each webhook's delivery status is indicated. A delivery is marked as failed if the URL doesn't respond within 10 seconds. Response records are purged after 30 days.
SonarQube Cloud doesn't retry to deliver failed webhook deliveries. You may use the Web API to implement an automatic redelivering mechanism.
If you downgraded your organization to the Free plan, existing webhooks are still visible on the UI but won’t be invoked by SonarQube Cloud. If you upgrade your organization, you regain access to them.
Monitoring your project's webhooks
You must be a project admin.
Proceed as follows:
- Retrieve your project.
- Go to Administration > Webhooks. The page shows the result and timestamp of each webhook's most recent delivery.
- To view the payload of the last delivery, select the three-dot menu at the far right of the webhook row.
- To view the results and payloads of earlier deliveries, select the three-dot menu at the far right of the webhook row.
Monitoring your organization's webhooks
You must be an organization admin.
Proceed as follows:
- Retrieve your organization.
- Go to Administration > Configuration > Webhooks. The page shows the result and timestamp of each webhook's most recent delivery.
- To view the payload of the last delivery, select the three-dot menu at the far right of the webhook row.
- To view the results and payloads of earlier deliveries, select the three-dot menu at the far right of the webhook row.
Securing webhooks
After you've configured your server to receive payloads, you want to be sure that the payloads you receive are initiated by SonarQube Cloud and not by attackers. You can do this by validating a hash signature that ensures that requests originate from SonarQube Cloud.
A basic authentication mechanism is supported by providing user/password in the URL of the Webhook such as https://myLogin:myPassword@my_server/foo.
Setting your secret
To set your secret in SonarQube Cloud:
- From the project or organization where you're securing your webhooks, navigate to the webhooks settings at Administration > Webhooks
- You can either select Create to create a new webhook or click an existing webhook's settings drop-down and select Update.
- Enter a random string in the Secret text box. This is used as the key to generate the HMAC hex digest value in the
X-Sonar-Webhook-HMAC-SHA256header. - Select Update.
Validating the received payload
After setting your secret, it's used by SonarQube Cloud to create a hash signature with each payload that's passed using the X-Sonar-Webhook-HMAC-SHA256 HTTP header. The header value needs to match the signature you are expecting to receive. SonarQube Cloud uses a HMAC lower-case SHA256 digest to compute the signature of the request body. Below is some sample Java code for your server. In this example, we are using the lib from apache commons-codec HmacUtils class.
private static boolean isValidSignature(YourHttpRequest request) {
String receivedSignature = request.getHeader("X-Sonar-Webhook-HMAC-SHA256");
// See Apache commons-codec
String expectedSignature = new HmacUtils(HmacAlgorithms.HMAC_SHA_256, "your_secret").hmacHex(request.getBody())
return Objects.equals(expectedSignature, receivedSignature);
}If the signatures don't match, then the payload should be ignored.
Adding parameters to the webhook payload
If you provide additional properties to your SonarScanner using the pattern sonar.analysis.*, these properties will be automatically added to the section "properties" of the payload.
For example these additional parameters:
sonar-scanner -Dsonar.analysis.buildNumber=12345would add this to the payload:
"properties": {
"sonar.analysis.buildNumber": "12345"
}Was this page helpful?