Connected mode
SonarQube for IDE is a free IDE extension that integrates with SonarQube Server. Like a spell checker, it highlights issues as you type.
Connected mode binds your SonarQube (Server, Cloud) project to a project open in SonarQube for IDE so that you can catch issues immediately, even before you commit them.
SonarQube for IDE is a free IDE extension that integrates with SonarQube (Server, Cloud) using connected mode. Like a spell checker, SonarQube for IDE highlights issues as you type. When an issue is identified, SonarQube for IDE provides you with clear remediation guidance so you can fix it before the code is even committed. In many cases, it also provides a quick fix that can automatically fix the issue for you.
Supported IDEs
SonarQube for VS Code will automatically identify and fix quality and security issues as you code with enhanced linting capabilities directly in your VS Code IDE.
Installation instructions
Supported Rules and languages
Connected mode setup and list of Connected mode benefits.
SonarQube for IDE integrates with most JetBrains IDEs including IntelliJ IDEA, CLion, GoLand, WebStorm, PHPStorm, PyCharm, Rider, Android Studio & RubyMine.
Installation instructions
Supported Rules and languages
Connected mode setup and list of Connected mode benefits.
SonarQube for IDE provides Visual Studio developers with a comprehensive in-IDE solution for improving the quality and security of the code they deliver.
Installation instructions
Supported Rules and languages
Connected mode setup and list of Connected mode benefits.
SonarQube for Eclipse will automatically identify and fix quality and security issues as you code with enhanced linting capabilities right in your Eclipse IDE.
Installation instructions
Supported Rules and languages
Connected mode setup and list of Connected mode benefits.
The supported languages vary by IDE. Check the Rules page for your IDE to learn which languages are supported out-of-the-box and which require the use of connected mode.
Though SonarQube for IDE can run local analyses in standalone mode, we highly recommend that you set up connected mode with SonarQube Server. Running SonarQube Server and SonarQube for IDE in connected mode provides additional valuable features.
Connected mode benefits
Combining SonarQube for IDE-supported rules with those supported by SonarQube Server allows you to analyze more languages and detect more issues. See Rules and languages for more information.
Highlight advanced issues (in the IDE) like injection vulnerabilities , detected by SonarQube Server. See Security-related rules for more information.
Use the same quality profile locally as is defined on SonarQube Server. See Understanding quality profiles for more information.
Apply settings, such as rule selection and file exclusion defined on SonarQube Server, to your local analysis.
Define specific Analysis parameters on SonarQube Server, and have those parameters applied locally.
Automatically suppress issues that are marked as Accepted or False Positive on SonarQube Server so that locally reported issues match those found on the server.
Use the SonarQube for IDE focus on new code features to concentrate detection of issues only in new code. See Quality standards and new code for more information.
Changes in your SonarQube Server quality gate will arrive in your IDE when you accept Smart notifications. See Understanding quality gates for more information.
Using the Open in IDE feature
If you’re using SonarQube for IDE (IntelliJ, Visual Studio, VS Code, or Eclipse), it’s possible to use the Open in IDE button to open most issues in the code editor, speeding up the time it takes to find and fix the issue. Simply select the Open in IDE button from SonarQube Server to view it in your IDE; you’ll be prompted to set up Connected Mode if the project is not already bound.
Opening Security hotspots using the Open in IDE feature is available for all of the supported IDEs. See Opening issues in your IDE for more details.
Reviewing issues in your IDE
Seeing an issue directly in the IDE can help you better understand its context. This is the purpose of the Open in IDE button that you’ll see as an authenticated user.
This feature is available if you’re using a compatible version and flavor of SonarQube for IDE. The project must be open in the appropriate IDE and bound to the server through connected mode. To learn more about managing issues locally, please check the SonarQube for IDE documentation for your IDE:
Investigating issues in SonarQube for VS Code
Investigating issues in SonarQube for IntelliJ
Investigating issues in SonarQube for Visual Studio
Investigating issues in SonarQube for Eclipse
Simply open a file of a supported language and start coding, and you will start seeing issues highlighted in your code. For example, here is SonarQube for VSCode:
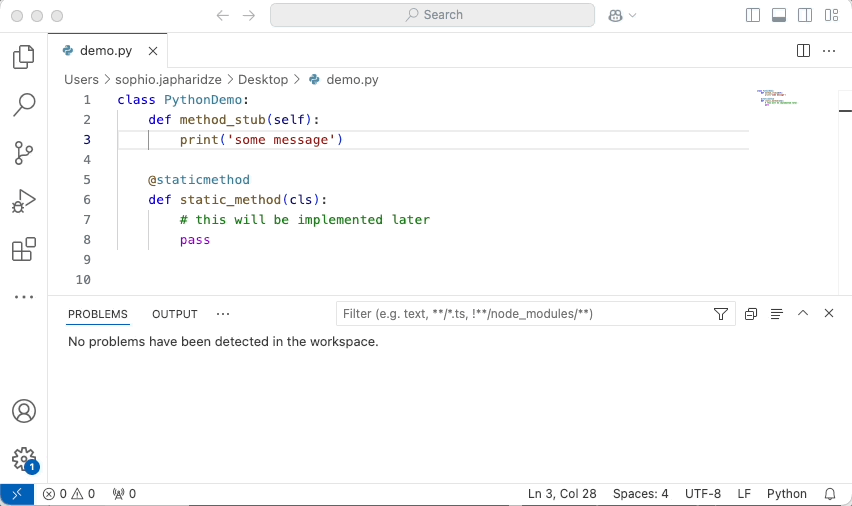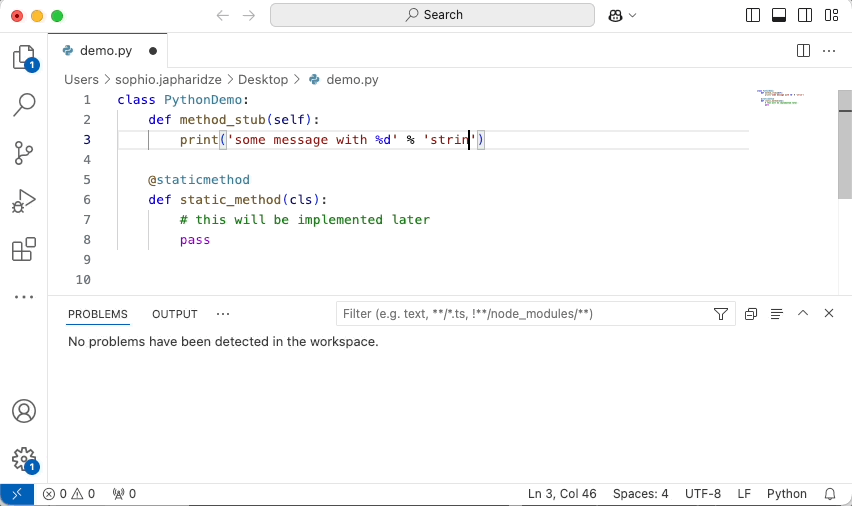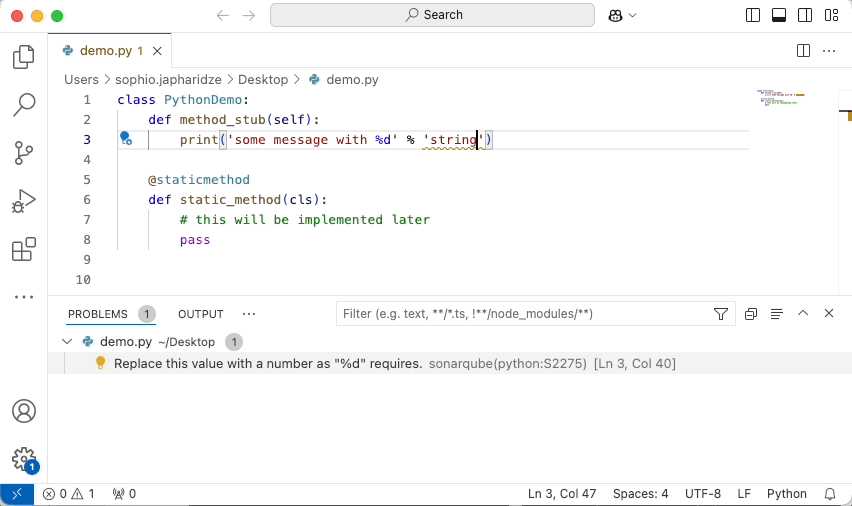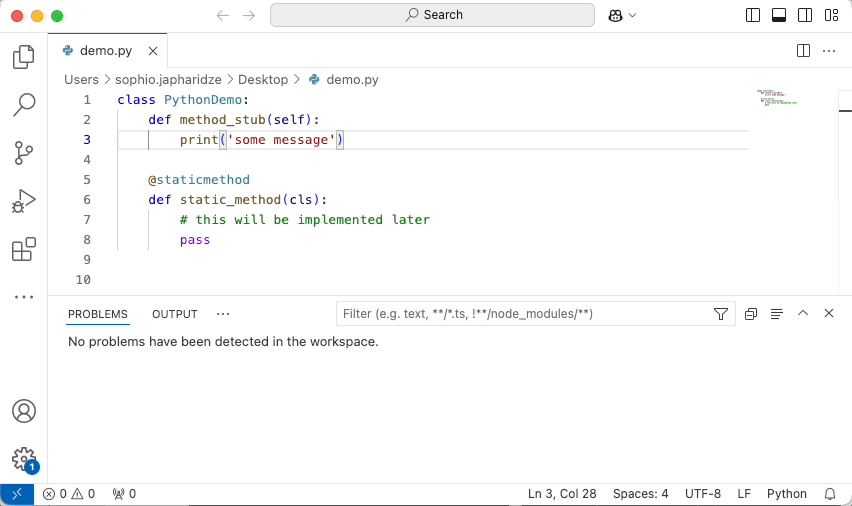
Keep in mind that the revision or branch analyzed by SonarQube (Server, Cloud) may not be the same as what you have opened in the IDE. In this case, SonarQube for IDE will do its best to locate the issue in your local code.
Commercial edition rules
There are rules that are available in SonarQube Server but not in SonarQube Community Build. These rules are available only in connected mode in SonarQube for IDE.
Understanding SonarQube for IDE usage
SonarQube Server Instance Admins can access an overview of users’ usage of SonarQube for IDE by going to Administration > Security > Users.
The Last SonarQube for IDE connection column indicates the last time the user used SonarQube for IDE in connected mode.
You can filter users based on their activity. The available options are:
All users
Active users with SonarQube for IDE: users of SonarQube for IDE in connected mode who were active at least once in the past 30 days.
Active users without SonarQube for IDE: users who have connected to SonarQube Server at least once in the past 30 days.
Inactive users: users who have not connected to SonarQube Server or used SonarQube for IDE in connected mode in the past 30 days.
Smart notifications
Connected mode allows SonarQube (Server, Cloud) to send smart alerts to individuals or teams when new issues are discovered. With everyone in the loop, issues can be addressed promptly, improving the overall software quality and delivery. You’ll receive smart notifications in your IDE when:
the quality gate status of a project open in your IDE changes
a SonarQube Server analysis raises new issues that you’ve introduced in a project open in your IDE
Each developer must individually activate or deactivate SonarQube for IDE smart notifications directly in SonarQube for IDE on the IDE side. When setting up connected mode for the first time, there’s a box to check to decide whether or not you want to receive Smart Notifications from SonarQube Server in your IDE.
For all the details about managing notifications, check the SonarQube for IDE documentation that matches your IDE:
Notifications in SonarQube for VS Code
Notifications in SonarQube for IntelliJ
Notifications in SonarQube for Visual Studio
Notifications in SonarQube for Eclipse
SonarQube for IDE - SonarQube Server version support policy
SonarQube for IDE enables users to establish a connection to the latest SonarQube Server version and to the latest LTA (Long-Term Active) version. When a new LTA version is released, we still enable connecting SonarQube for IDE to the previous LTA version for a certain period of time (currently 9 months after the latest LTA release) to allow enough time for organizations to update their SonarQube Server version.
The 8.9LTA reached its support expiration date (in November ’23).
For more information about long-term support of SonarQube Server, check out our page describing the Release cycle model. Review your SonarQube for IDE-specific requirements for version-to-version differences.
Troubleshooting unexpected analysis results
Unexpected analysis results
Observing different analysis results between SonarQube (Server, Cloud) and SonarQube for IDE can have different causes.
Some issues might be detected by a third-party
Due to extensive resource requirements, injection vulnerability and some advanced bug detection rules are ignored by SonarQube for IDE. Please check the analyzer (PMD, Checkstyle, ESLint, PyLint, …). SonarQube for IDE will only run rules from Sonar analyzers including custom rules extending SonarSource analyzers. See Adding coding rules for more information. Third-party analyzers usually have their own IDE integration, so we have no plan to run them in SonarQube for IDE.
Your test files might be mistaken as source files
Test files can be defined on the server or in the IDE, and when running in connected mode, these test sources will be used by SonarQube for IDE. Each SonarQube for IDE flavor has its own way of detecting which file is considered a test file; in SonarQube for IntelliJ, you must define your test files as a Test Sources Root. To define test files on the server, see the Setting analysis scopeIntroduction page.
Some complex rules are not run in SonarQube for IDE
Due to extensive resource requirements, injection vulnerabilities and some advanced bug detection rules are ignored by SonarQube for IDE. See SonarQube for IDE roadmap for a list of features and enhancements on the horizon.
Only line-level issues are reported
Such issues are not displayed in SonarQube for IDE, only in SonarQube Server.
When analyzing Java files, the analyzer might need some context for some issues to be found
In IntelliJ, there is no incremental compilation of the .class files found in the compiler output folder; these are only produced or refreshed when the project is built. The workaround is to simply build your project with the green hammer (when using SonarQube for IntelliJ) in the top-right toolbar. The project should be built on a regular basis to keep the compiled files up-to-date and overcome this known limitation.
Related online learning
Last updated
Was this helpful?

